VMware Avi Load Balancer and Datascripts
The VMware Avi Load Balancer enables traffic management through Datascripts. In this blog post, we’ll explore a specific use case where traffic from VMware Aria Operations Nodes is directed to specific VMware Cloud Director (VCD) cells, while regular user traffic is routed to different cells. This use case can be especially beneficial when a six cell design is being used.
Use Case: Separate Traffic for Operations and Users
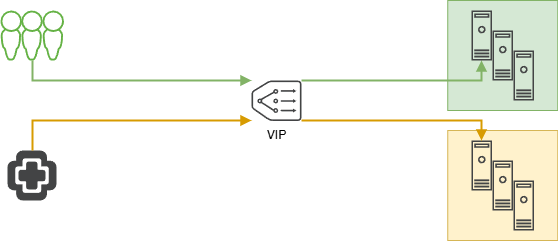
In this scenario, the VMware Cloud Director setup consists of six cells, all sitting behind a single virtual IP (VIP).
Key Requirement:
- Traffic from VMware Aria Operations Nodes should be directed exclusively to cells 4–6.
- Regular user traffic should be distributed across cells 1–3.
- The six cells are split between two separate backend pools.
Architecture Overview
- Virtual IP (VIP): A single IP address represents the access point for all traffic.
- Backend Pools: Contain all six VCD cells.
- Cell Groups:
- Cells 1–3: Reserved for “normal” user traffic.
- Cells 4–6: Reserved for operations traffic.
- Goal: A DataScript will dynamically differentiate traffic based on criteria such as source IP and routes it to the appropriate cell group.
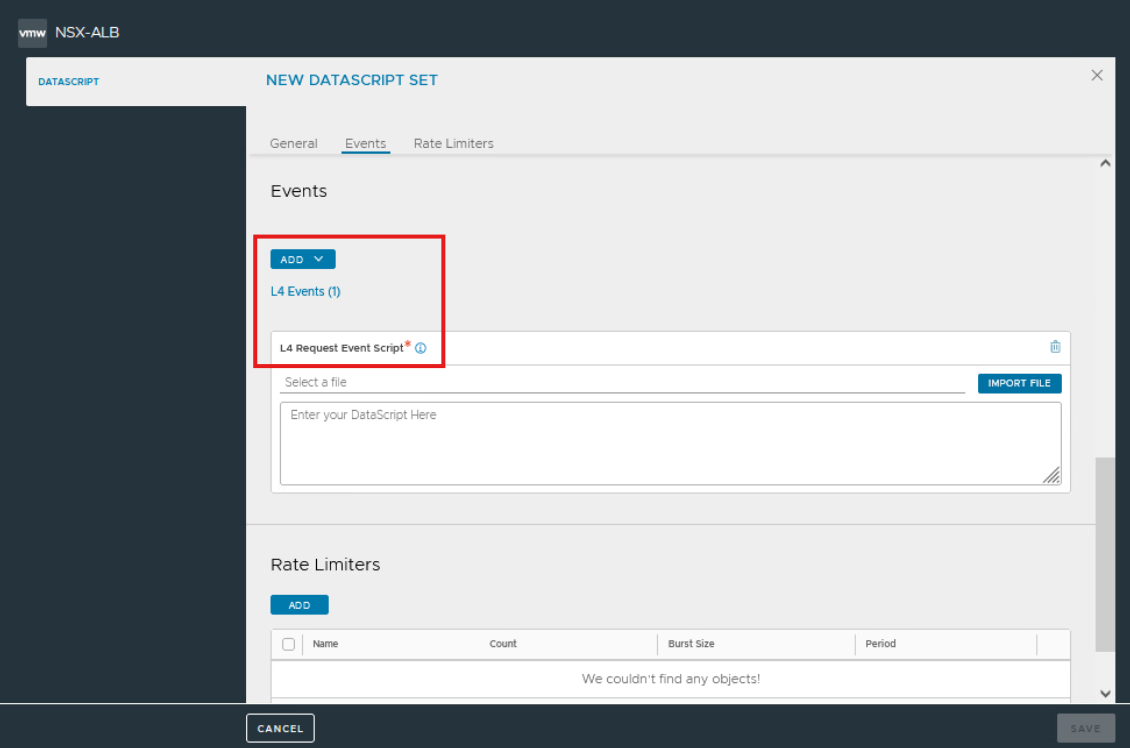
Implementation with Datascripts
To achieve this use case, we’ll use a Datascript that is executed by the Avi Load Balancer. The script checks whether an incoming request originates from a known Aria Operations Node and redirects the traffic to the target pool (cells 1–3 or cells 4–6).
The following Datascript differentiates traffic based on the source IP address:
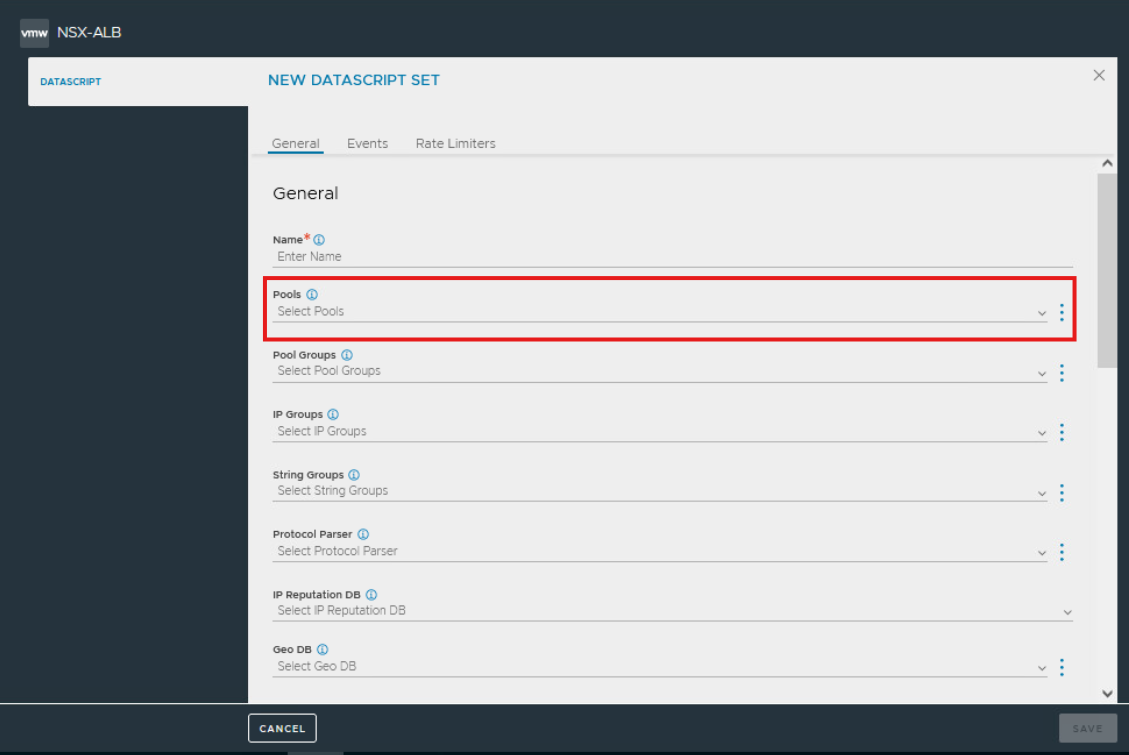
Prerequisites
-
Create a dedicated pool for Operations traffic and user traffic
-
Select the pools to utilize them within the datascript
-
create and L4 Request Event

-
Script in Lua
// Datascript for Traffic Steering
local client_ip = avi.vs.client_ip()
// Define IP addresses of Aria Operations Nodes
local operations_nodes = "x.x.x.x"
// Backend pool configuration
local pool_operations = "VCD-LoadBalancer-*ID*-*Poolname" // VCD cells 4-6 for operations traffic
local pool_users = "VCD-LoadBalancer-*ID*-*Poolname" // VCD cells 1-3 for user traffic
// Select target pool
if client_ip == operations_nodes then
pool_operations
return
else
pool_users
return
end
Script Details
- Retrieve Client IP:
avi.vs.client_ipextracts the source IP address of the request.
- Define Operations Nodes:
- Known IP addresses of Aria Operations Nodes are listed in a variable.
- Assign Pools:
- Traffic from operations nodes is routed to the cells 4–6 pool.
- All other traffic (e.g. from users) is routed to the cells 1–3 pool.
Validation and Monitoring
Just to be sure that everything works as designed, check the following if needed:
- Log Inspection: Review Avi Load Balancer logs to confirm if the redirect works.
- Performance Monitoring: Use Avi’s monitoring features to track the utilization of each cell group (avi pools).
- Fallback Mechanism: Implement fallback strategies to redirect traffic to an alternative group if a pool becomes unavailable. Otherwise, clients may not be able to access the VCD.
Conclusion
The VMware Avi Load Balancer, coupled with Datascripts, offers a nice way to precisely control traffic in your environments. In many Use Cases Avi Policies may be sufficient. Take a look at them both and consider what is more suitable for your use case.
Access the VMware Lab Platform through the provided links below and try it out yourself.
Note
Useful Links: